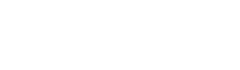HEEL PAIN IN CHILDREN
Sever’s is most common in 9 - 12 year olds. It’s sore to squeeze the bone at the base of the Achilles where it attaches onto the heel. It’s not something that can be seen - it never seems to look red or swollen. It’s worse after sprinting, jumping, and hopping. It settles with rest. It is an overuse injury so it’s common in pre-season, or anytime training loads increase too quickly. My kids get it when they do extra sessions in running spikes or footy boots, without the normal heel support of their running shoes. It’s an overuse injury from excessive loads.
OVERUSE INJURY
When we talk about excessive loads it can be “external” load such as:
I think the running pace is the more powerful multiplier in this list. Extra sprint sessions will do it. My kids got sore once when we did a boot-camp session with a novel plyometric exercise - split jumps. There are also “internal” variables that determine our ability to cope with the training load:
My kids definitely are more prone to Sever’s if they’ve had a couple of late nights that week. And, if they’re having a growth spurt, their bodies are busy spending resources on growing rather than recovering from the stress of a training session. NATURAL RECOVERY
Text books say that Sever’s disease is self-limiting because the growth plate eventually fuses by the age of 15 or 16. But I don’t think there’s anyone who would be happy to just let it run its course until then. It is usually sore enough to stop you participating in sport, so it needs treatment.
WHAT DO WE DO?
I used to put kids with heel pain in orthotics, until I read this research which confirms that a simple heel wedge is more effective than orthotics for Sever’s disease.
I get them to do an isometric Achilles strengthening program which also helps with pain control. But ultimately recovery comes down to load management. Load management means reducing the excessive loads. So this could be:
And aid recovery with:
With these type of overuse injuries, I interpret "soreness" as essentially the same thing as "tiredness". If they've been training more, sleeping less, or growing more, we would expect some "tiredness". If they were tired what would be the treatment?... Sleep more and train a bit less.
TENDON PAIN
Tendinopathy (tendon pain) is very common. They are the most common type of overuse injury (ref). Achilles tendinopathy affects the majority of runners (ref) and is the reason 16% of athletes have to stop sports participation (ref).
There are a range of commonly prescribed treatment options for tendinopathy, but very few are supported by quality, randomised, prospective, placebo-controlled trials. SO WHAT DO I DO?
Considering all the available treatment options, above anything else, I always recommend:
WHAT ABOUT INJECTIONS?
Having mapped out a management plan, patients will routinely ask my opinion on getting an injection. They may have had a friend for whom an injection worked well, or the GP has suggested it as an option, or they’ve had one before and it worked.
There are a range of drugs to inject into or around a tendon, depending on who you are referred to:
CORTICOSTEROIDS
Corticosteroids are an anti-inflammatory medication injected around the tendon to decrease pain that is caused by inflammation (although it is now thought that inflammation does not play a significant role in tendon pain). Corticosteroid injections have historically been commonly prescribed but more recently their use is controversial. Repeated corticosteroid injections can weaken the tendon and increase the risk of rupture. Corticosteroid injections are good at relieving pain in the short term (2-6 weeks) however, there is strong evidence that long-term outcomes (> 6 months) are worse than other conservative treatments or no treatment at all (ref).
"The best systematic review evidence shows that local corticosteroid injections are not effective for tendinopathies after the first few weeks, and produce worse long-term outcomes compared to other treatments" (ref) PROLOTHERAPY / SCLEROTHERAPY
Prolotherapy injections act as an irritant causing an inflammatory response then scarring of the nerves that transmit pain. There is no solid support in the medical literature for this procedure for the treatment of tendinopathies. A randomised controlled trial of polidocanol injections showed the potential to reduce tendon pain in patients with chronic painful mid-portion Achilles tendinopathy (ref). However, a systematic review found limited results for use of prolotherapy in sports related soft tissue injuries (ref).
AUTOLOGOUS BLOOD INJECTIONS
The rationale of autologous blood injection consists of enhancing tendon healing through collagen regeneration and the provision of cellular mediators. Good experimental models are lacking, and clinical application is anecdotal. A 2013 randomised controlled trial investigating the efficacy of autologous blood injections as a treatment for mid-portion Achilles tendinopathy concluded they did not reduce pain or improve function any more than a strengthening program. (ref)
HIGH-VOLUME INJECTIONS
The suggested mechanism of high-volume injections is the mechanical disruption of local tissues then stimulates a healing response. One study (ref) has shown that high-volume injection of normal saline solution, corticosteroids or anaesthetics reduces pain and improves short and long-term function in patients with Achilles tendinopathy. However, more research is required.
PLATELET RICH PLASMA (PRP)
Platelets are naturally occurring in your blood, where they play an important role in healing damaged tissue, so superficially it’s inherently appealing to just add more of them to the sore spot. PRP injections are particularly trendy at the moment and it’s easy to find someone who will tell you they work well. Unfortunately, research concludes there is no benefit to PRP injections. This study found PRP injections do not improve plantar fasciopathy pain or function. This study concluded there is insufficient evidence to support the use of PRP for treating musculoskeletal soft tissue injuries. This systematic review found strong evidence against platelet-rich plasma injections for tennis elbow. This study found PRP did not improve tendon structure. This meta-analysis found no greater clinical benefit of PRP over placebo or dry needling for tendinopathy.
SO…
Would I have any of these injections, or would I recommend them to my patients, friends, or family? Well it depends. In my experience some people get some benefit some of the time. HOWEVER, these injectables are not consistently effective and their use is mostly not supported by research. I suggest that patients try the strengthening program and the results will be overall better in the long term.
WHY DO THE INJECTIONS WORK FOR SOME PEOPLE?
I’ve been frustrated with a couple of patients that cancelled their follow-up appointment and, when I phoned and asked what had happened, they’ve had an injection and now feel fine. My conclusion is the injections don’t work, but if you were sore and now you’re not, your conclusion would be they do work. So what is it?..
REGRESSION TO THE MEAN
Most people seek treatment when they are at their worst. By definition the only possible change from being as bad as at can be, is an improvement. Was it the injection working, or was it getting better anyway?
NATURAL HISTORY
Some conditions are self limiting and will just get better by themselves. Did the injection work, or was it about to get better anyway?
PLACEBO
SUMMARY
I understand that getting an injection seems like a much easier option than doing 12-weeks of strengthening exercises, but in the long run, a strengthening program is the thing that actually works.
TL;DR
If treating tendon pain was as easy as getting an injection then that’s what everyone would do first. Unfortunately it’s not as easy as that.
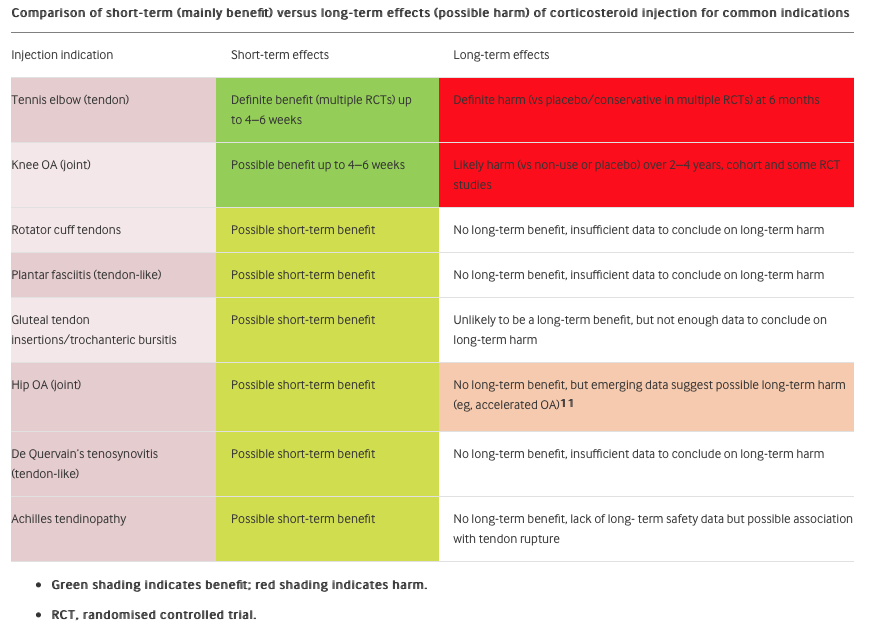
Research Summary: The ‘Best Practice Guide to Conservative Management of Patellofemoral Pain’: incorporating level 1 evidence with expert clinical reasoning (Barton et al, 2015). Patellofemoral pain (PFP) is a common cause for knee pain in general practice and sports settings. Pain is aggravated by running, stairs, and squatting. The majority of suffers report an onset of pain in early adolescence and chronic ongoing pain for up to 20 years. A number of high-quality reviews covering conservative interventions for PFP provide greater guidance for research and clinical practice. Four key principles to ensure effective management include: (1) PFP is a multifactorial condition requiring an individually tailored multimodal approach. (2) Immediate pain relief should be a priority to gain patient trust. (3) Patient empowerment by emphasising active over passive interventions is important. (4) Good patient education and activity modification is essential. Research supports a multimodal treatment approach including:
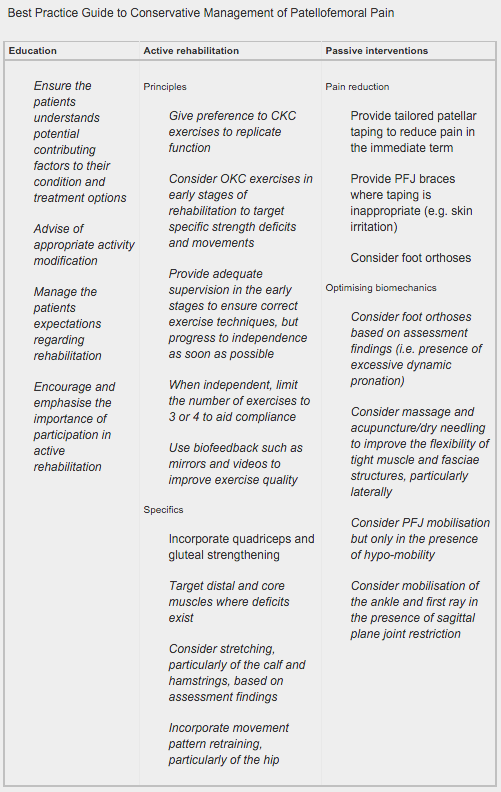
The ‘Best Practice Guide to Conservative Management of Patellofemoral Pain’ has been based on a combination of contemporary level 1 evidence and the analysis of international experts’ clinical reasoning: ACL Rehabilitation Guide (available here) A criteria driven ACL rehabilitation protocol and guide for both clinicians and people who have undergone a surgical reconstruction of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL). Author: Randall Cooper
Hamstring injuries: prevention and treatment — an update (Peter Brukner, 2015)
TLDR Summary:
Recommendations:
Example Exercises:
Ankle sprains are the most common sports injury.
After an initial ankle sprain, athletes are prone to re-injury of the same ankle. The risk of suffering an ankle sprain is doubled in the year following initial injury. Common interventions aimed at preventing ankle sprains include taping, bracing, muscle strengthening, and balance training. Taping and bracing have shown to be effective prevention for ankle sprains, however disadvantages include hindering performance, loosening with activity, and skin irritation. A 2015 systematic review and meta-analysis from La Trobe University has concluded that balance training programmes are effective at reducing the rate of ankle sprains in sporting participants, particularly those with a history of ankle sprains. Approximately 17 sporting participants, or 13 participants with a history of ankle sprain need to undergo balance training in order to prevent one future ankle sprain.
New research, a 2015 systematic review, concludes that massage therapy reduces pain and improves function in the short term, for shoulder pain, low back pain, and osteoarthritis of the knee.
SUMMARY: Musculoskeletal disorders cause pain and disability in a substantial proportion of the population. The most affected areas of the body are low back, neck, shoulder, and knee. Massage therapy is one of the earliest therapeutic tools used to relieve pain, and is a widely accepted treatment for musculoskeletal disorders. Massage therapy plays a major role in physiotherapy practice. The specific mechanisms of action of massage therapy are unknown, but various physiological responses include: increased lymph flow, a parasympathetic neural response, increased clearance of blood lactate, effects on the immune system, cognition, & pain. Massage therapy seems to produce local biomechanical changes which increase neural activity at the spinal cord, affecting mood, pain perception, anxiety, and depression. http://www.journalofphysiotherapy.com/article/S1836-9553(15)00058-2/fulltext
Tendon pain is the most common gradual-onset, overloading injury. Mechanotherapy / exercise is the most beneficial treatment option.
Eccentric exercises have been commonly prescribed over the last decade, following the pain-provoking Alfredson programme of 3 x 15 reps, twice/day. It sometimes works very well. The last few years I’ve favoured isometric exercise as an initial treatment - partly because of personal experience with Achilles, patellar, and lateral elbow tendon issues, & recommendation from Jill Cook & Craig Purdham at the AIS.
New research adds some support to isometric exercise as a treatment for tendinopathy, concluding it reduces tendon pain and improves strength. The authors delve in to all the “hows” & “whys” of how it works in their discussion, and to be honest it’s a bit technical for my understanding.
The research protocol uses 5 reps of a 45 second contraction, at a 70% effort. I prefer a more gentle contraction of 50% effort, but a longer hold of at least a minute, and I like a larger total volume of at least 10 minutes/day. Obviously it’s hard to define what the perfect dosage is for exercise, & volume could be adjusted depending on results. I like isometrics because:
|
�
Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|
|
|
MENU
|
INJURY INFO
|
INJURY INFO
PHYSIO MOSMAN |
Copyright© 2024| Fit As A Physio | ABN 62855169241 | All rights reserved | Sitemap




 RSS Feed
RSS Feed